Understanding Your Oral Anatomy and Managing Common Dental Issues
Introduction
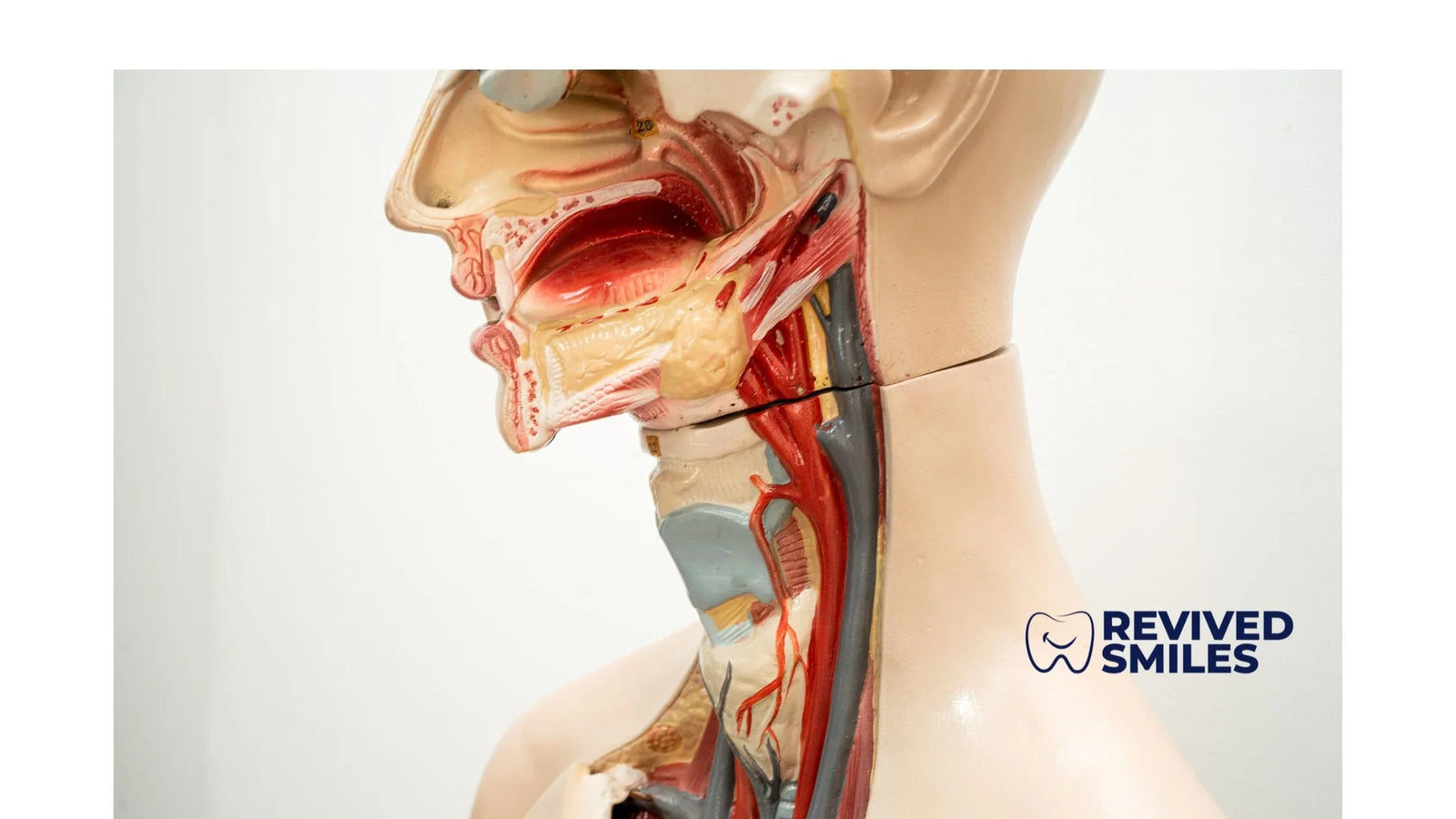
Understanding your oral anatomy is crucial for maintaining good dental health and preventing common dental issues such as missing teeth and cavities. The mouth is a complex system that plays a vital role in digestion, communication, and overall health. This article delves into the basics of oral anatomy, the precautions necessary to maintain a healthy mouth, and the solutions for common dental problems.
The Basics of Oral Anatomy
1. Teeth:
Teeth are essential for breaking down food into smaller pieces, making it easier to digest. There are four main types of teeth:
- Incisors: These are the front teeth used for cutting food.
- Canines: Located next to the incisors, these teeth tear food.
- Premolars: These have a flat surface for crushing food.
- Molars: These are the largest teeth used for grinding food.
2. Gums:
Gums are the soft tissue that surrounds and supports the teeth. Healthy gums are pink and firm, and they play a crucial role in protecting the roots of the teeth and the bone underneath.
3. Tongue:
The tongue is a muscular organ that aids in tasting, swallowing, and speaking. It is covered with tiny bumps called papillae, which contain taste buds.
4. Salivary Glands:
These glands produce saliva, which helps in digestion, keeps the mouth moist, and aids in cleaning the mouth by washing away food particles and bacteria.
5. Jawbone:
The jawbone supports the teeth and provides the structure necessary for chewing and speaking.
Common Dental Issues and Their Precautions
1. Cavities:
Cavities, or dental caries, are caused by the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Plaque produces acids that can erode the enamel and create holes in the teeth.
Precautions:
- Regular Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary snacks and drinks, as sugar feeds the bacteria that cause cavities.
- Dental Visits: Regular check-ups with your dentist can help detect and treat cavities early.
2. Gum Disease:
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. It starts with gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Precautions:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to remove plaque.
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking increases the risk of gum disease.
- Regular Dental Visits: Professional cleanings can help prevent gum disease by removing tartar (hardened plaque).
3. Missing Teeth:
Missing teeth can result from trauma, decay, or gum disease. They can affect your ability to chew, speak, and even your self-esteem.
Precautions:
- Protective Gear: Wear mouthguards during sports to prevent injury.
- Prompt Treatment: Address cavities and gum disease promptly to prevent tooth loss.
Solutions for Common Dental Issues
1. Fillings and Crowns:
For cavities, dentists can remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill it with materials like amalgam or composite resin. Crowns are used for more extensive decay, covering the entire tooth to restore its shape and function.
2. Root Canal Therapy:
If decay reaches the tooth's pulp (inner tissue), a root canal may be necessary. This procedure removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth to prevent further infection.
3. Dental Implants:
For missing teeth, dental implants are a popular solution. They involve surgically placing a titanium post into the jawbone, which acts as an anchor for a replacement tooth.
4. Dentures and Bridges:
Dentures are removable replacements for missing teeth, while bridges are fixed prosthetics that replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring to adjacent teeth.
5. Periodontal Treatment:
For gum disease, treatment may involve deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary.
Conclusion
Maintaining good oral health involves understanding your oral anatomy and taking proactive measures to prevent common dental issues like cavities and gum disease. Regular dental visits, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy diet are essential in keeping your mouth healthy. If dental problems do arise, there are numerous solutions available, from fillings and crowns to dental implants and periodontal treatment.
By staying informed and vigilant, you can ensure that your teeth and gums remain healthy, functional, and beautiful throughout your life.
Sources:





Leave a comment